MCP Architecture & Mechanics
High-Level Architecture
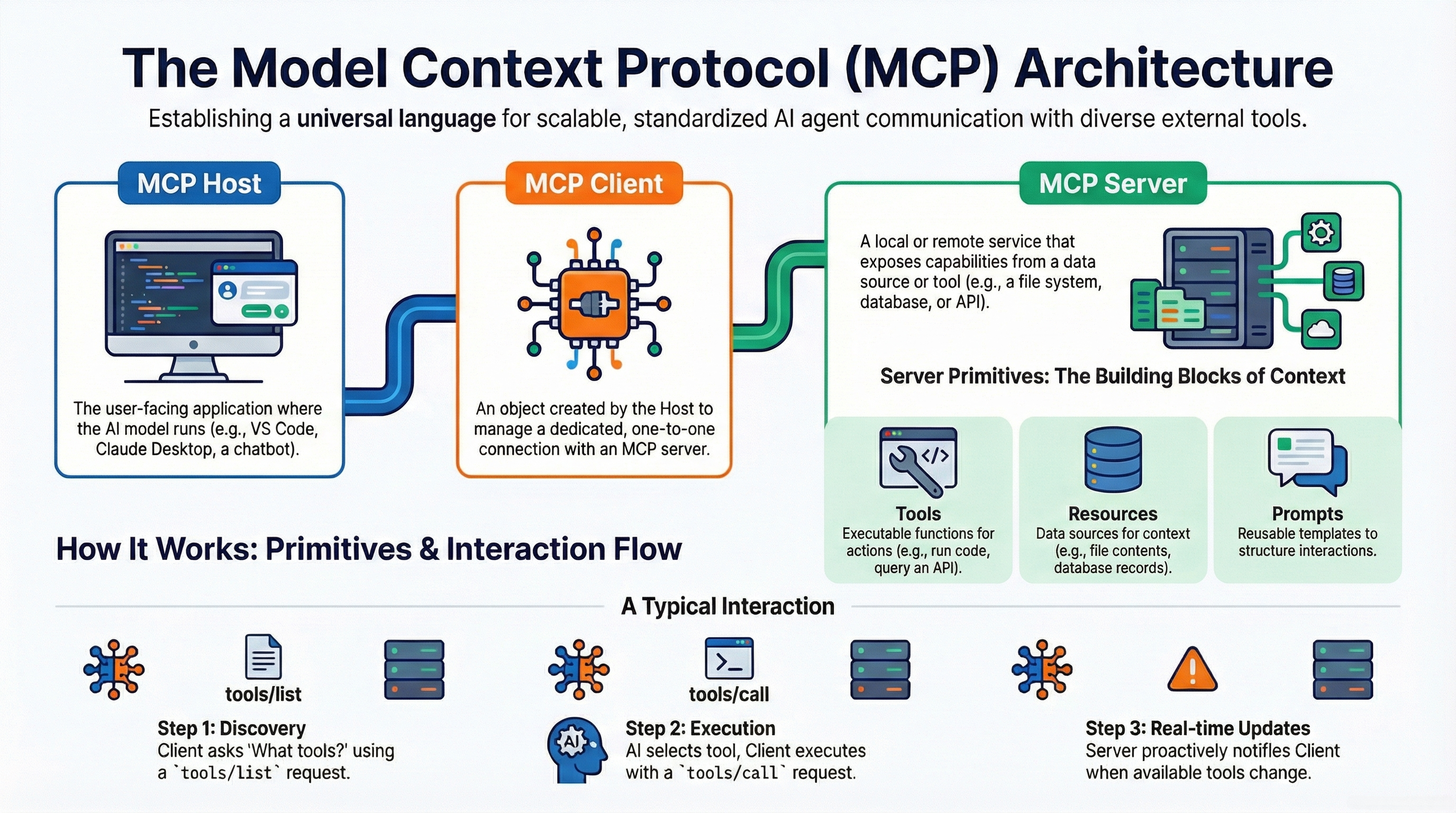
The Model Context Protocol operates on a distinct Client-Host-Server model designed to separate the AI's reasoning logic from the specific implementations of external tools.
-
1MCP Host: The user-facing application (e.g., Claude Desktop, IDE) managing connection lifecycle and security boundaries.
-
2MCP Client: Embeds within the Host, translating LLM intent into structured JSON-RPC requests.
-
3MCP Server: Exposes capabilities (tools/resources) and acts as the gateway to external services.
Transport Layers
MCP is transport-agnostic but primarily defines two standard mechanisms:
🖥️ Stdio (Standard I/O)
For local, secure environments
- Mechanism: Subprocess creation
- Pros: Ultra-low latency, high security
- Cons: Local machine only
☁️ HTTP with SSE
For cloud & distributed agents
- Mechanism: Server-Sent Events + POST
- Pros: Scalable, firewall-friendly
- Cons: Higher latency, auth required
Server Lifecycle
An MCP server's life involves four key stages:
Define logic
Local/Cloud
Handle requests
Security patch
Automation: The AutoMCP Revolution
AutoMCP addresses the "boilerplate" problem by compiling OpenAPI Specifications into functional MCP servers.
Performance & Optimization
The Latency Challenge
While MCP standardizes connection, it introduces a significant engineering challenge: Context Bloat.
The Problem: "Context Pollution"
When an agent connects to an MCP server, it typically loads:
- Tool Definitions: Schemas describing every tool.
- Results: Full output of every tool call.
- History: The entire dialogue.
The Solution: "Code Execution" Paradigm
To solve this, the industry is shifting from Direct Tool Calling to a Code Execution (or "Code Mode") model.
| Feature | Direct Tool Calling | Code Execution Paradigm |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanism | LLM outputs JSON to call tool. | LLM writes a script to call tools. |
| Context | High (Schemas + Results) | Low (Just libraries) |
| Efficiency | 150,000 tokens (Example) | 2,000 tokens (98.7% Less) |
Old Way (Direct)
"I will callread_filefor 'data.csv', then I will callfilter_data, then I will callsummarize."
New Way (Code)
# Agent-generated code
import pandas as pd
from mcp_tools import fs
# Read & Process in ONE go!
df = pd.read_csv(fs.get_path("data.csv"))
print(df.describe())Optimization Best Practices
- Limit Context: Use "router" agents to select toolsets; don't dump everything at once.
- Summarization: Summarize tool outputs before adding to history.
- Prefer Code Mode: For data-heavy tasks, write and execute code instead of API calls.